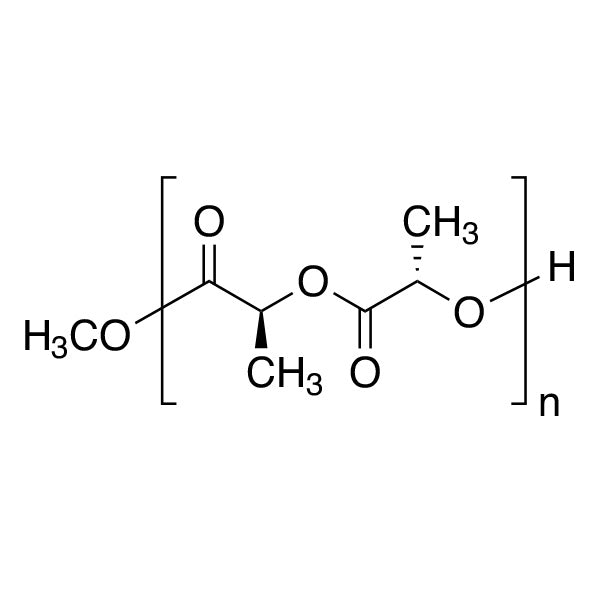
Poly(L-lactide), IV 2.4 dL/g
Product Number:
-
26405
Product Description
Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA), IV 2.4 dL/g
Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a bioresorbable and biodegradable polymer widely studied in the biomedical industry due to its strong biocompatibility profile and favorable mechanical properties. It is commonly used in research and development of resorbable medical devices such as sutures, bone fixation constructs, tissue scaffolds, and polymer- based drug delivery systems.
PLLA is increasingly evaluated in tissue engineering research, where its structural integrity and surface characteristics support investigations into cell attachment, growth, and tissue regeneration under controlled laboratory conditions.
The biodegradation of PLLA is primarily driven by hydrolysis of ester linkages. Degradation rate is influenced by multiple factors, including molecular weight, material thickness and geometry, processing history, pH, exposure to enzymes, and other biological and environmental conditions.
Polysciences offers a range of PLA and PDLA homopolymers and copolymers with varying molecular weights to support diverse research and formulation needs.
Key Properties
- Polymer type: Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) (PLA homopolymer)
- Intrinsic viscosity (IV): 2.4 dL/g
- Biodegradation mechanism: Hydrolysis of ester linkages
- Mechanical profile: Commonly associated with higher mechanical integrity (application-dependent)
- Biocompatibility: Well documented in biomedical literature
Applications
- Resorbable medical device research (sutures, fixation constructs, implantable prototypes)
- Tissue engineering and scaffold development
- Drug delivery system research and long-term degradation studies
- Polymer processing, extrusion, and materials characterization studies
Synonyms
- PLLA
- Poly(L-lactic acid)
- Poly(L-lactide)
- PLA (L-form)
FAQs
Common questions about Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA), IV 2.4 dL/g.
-
What is Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) used for?
PLLA is widely used in biomedical materials research, particularly for resorbable medical device concepts, tissue scaffolds, and polymer-based drug delivery systems.
-
How does PLLA biodegrade?
PLLA primarily degrades through hydrolysis of ester bonds in the polymer backbone. The resulting degradation rate depends on molecular weight, geometry, and environmental conditions.
-
What does an intrinsic viscosity (IV) of 2.4 dL/g indicate?
Intrinsic viscosity is an indirect measure of polymer molecular weight. An IV of 2.4 dL/g generally corresponds to a relatively high molecular weight PLLA grade, depending on test conditions.
-
What factors affect PLLA degradation rate?
Degradation rate can vary with molecular weight, crystallinity, processing history, material thickness, pH, temperature, and biological exposure such as enzymes.
-
How is PLLA different from PLGA?
PLLA is a homopolymer composed solely of lactide units, while PLGA contains both lactide and glycolide. Glycolide incorporation generally increases hydrophilicity and accelerates degradation compared to PLLA.